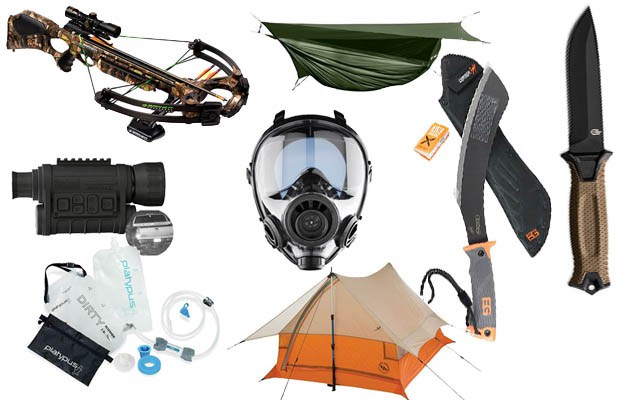
Top 20 Best Prepper Gifts for any Survival Situation
Do you have a prepper on your shopping list? The occasion doesn’t matter really. It could be Mother’s Day, Father’s Day, Christmas or Hanukkah, birthdays or just because. But sometimes finding the perfect gift for the prepper who has everything can be tough. Why is that? Well, most preppers already have some of the gear (toys) they deem valuable and it may never have even crossed your mind that a gas mask would be something they wanted. Who knew how excited they would get over a hand crank radio with a built-in solar charger?
Well if you are looking for the best prepper gifts for that special person on your list, you have come to the right place. There are other lists of survival items on the internet and the usually pop up close to those big shopping holidays. Some of the best prepper gear lists are broken down by dollar amount, but I wanted to do a little something different and recommend items based upon the type of disaster your prepper is planning on. If you know what gets their survival juices flowing, we have some ideas below that might make your present, the best prepper gift they have ever received. Hey, they might even share it with you too.
Disaster Scenario #1 – Weekend Vacation Chaos
This could also be the rush evacuation from oncoming flood waters, approaching wildfires, car wreck in a blizzard or rioting on the next block over. What are some of the best prepper gifts for the survivalist who wants to be ready to go in a moment’s notice? What could they possibly carry with them wherever they may roam that could offer an advantage if they encountered trouble?
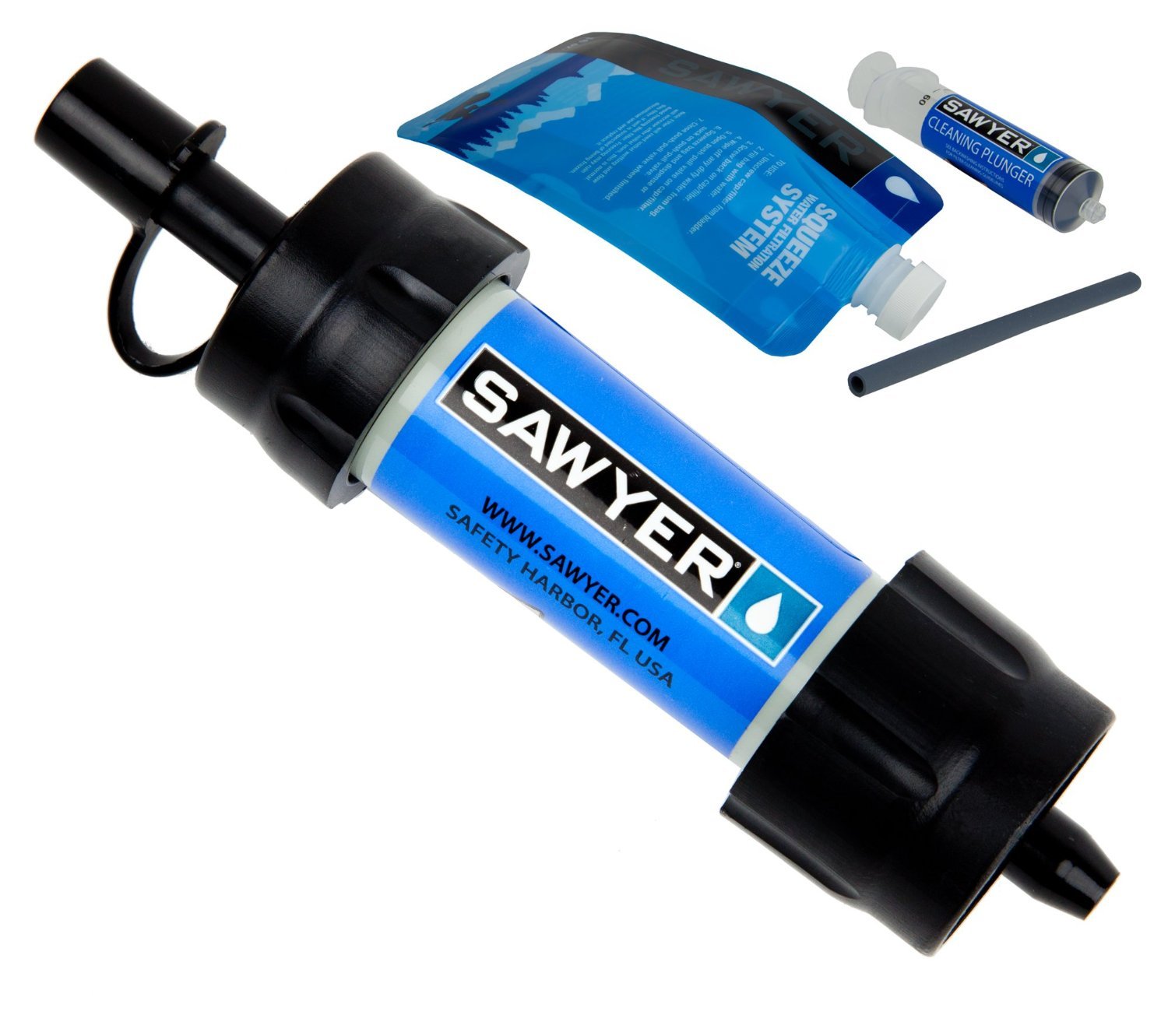
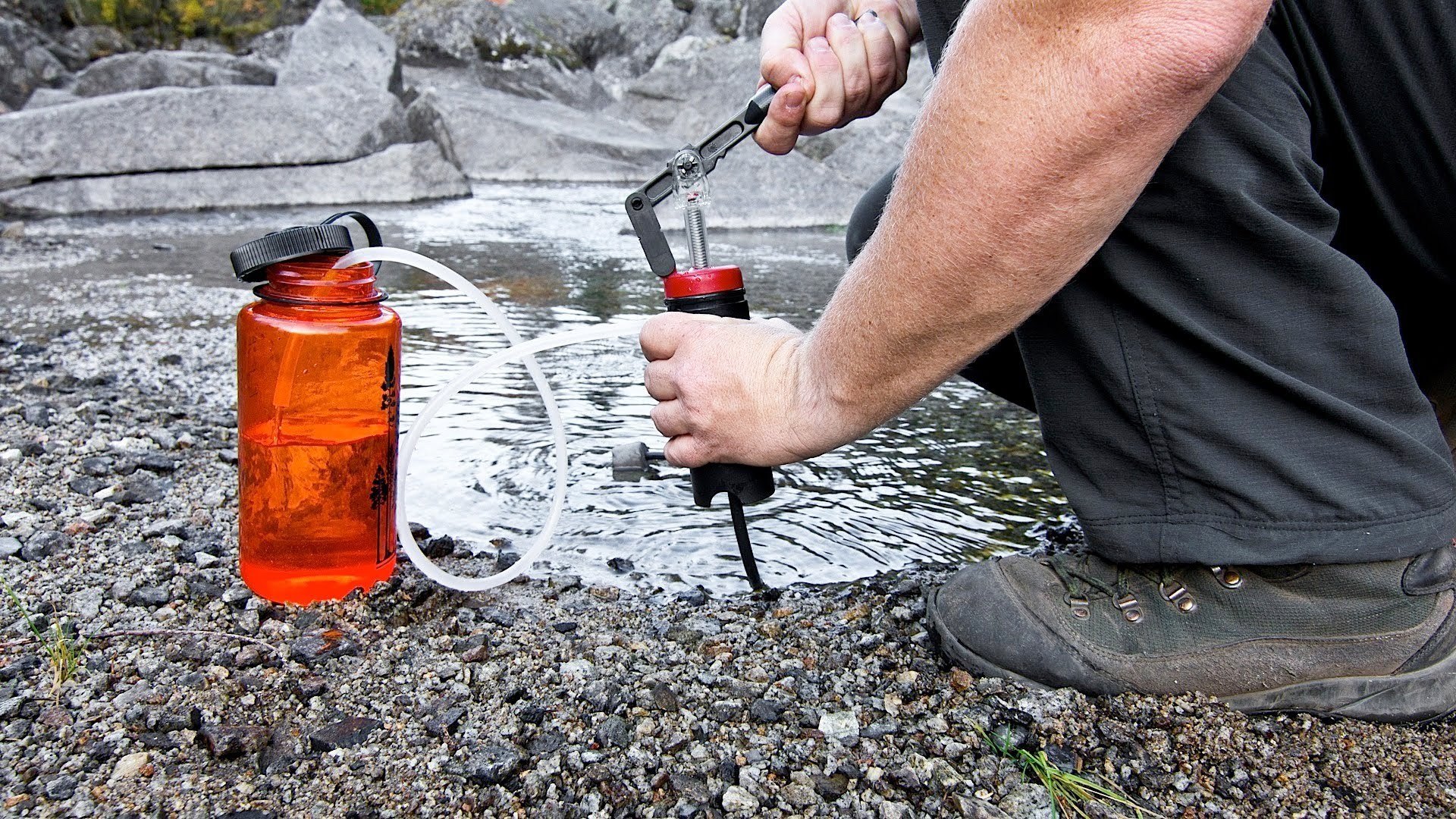
Water – Sawyer Mini – When it comes to survival water filtration, there aren’t any other options I can think of that are as durable, lightweight and compact as the Sawyer Mini. I have these as backup filtration in my Bug Out Bags and when we go backpacking. This little 2 ounce wonder of a water filter will give your prepper the ability to make up thousands of gallons of fresh drinking water from even the nastiest of sources.
Food – Emergency Rations – In a survival situation, an empty stomach can be a demoralizer but putting a sandwich in your carry on isn’t usually recommended either. Emergency rations add a little weight to your gear, but the right ones like Mainstay are virtually impervious to extremes in temperature and one pack gives your favorite survivalist 3600 calories of living saving goodness. Well, it is 3600 calories and that brick can save their life if food options are scarce. Yes, you can certainly live for longer than a weekend without any food, but who wants to do that?

Pack it in your bag and when you need it, you will have 3600 calories that could be enough to last you through the disaster.
A different prepper gift option could also be used backpacking and would probably taste better. For grid-down meals that are pretty tasty, a couple of Mountain House entrees fit the bill nicely. I got something like this for my Dad, who is not a prepper and didn’t see the humor to boot for last Father’s Day. Any freeze-dried foot you get will need to have water, usually hot water added to it so it can reconstitute. A Jet Boil is a great system for backpacking meals that works just as well if you have had some type of disaster as long as you have the right fuel.
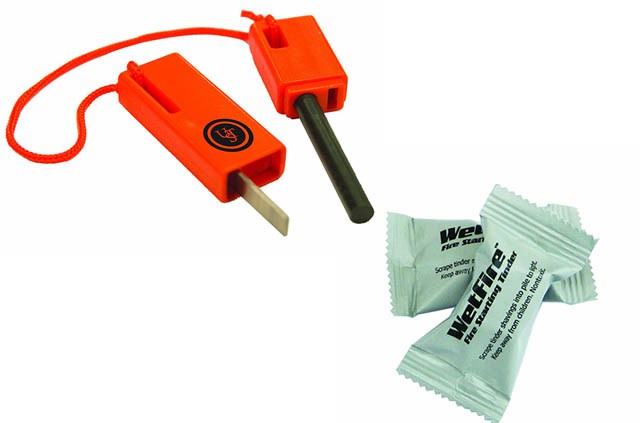
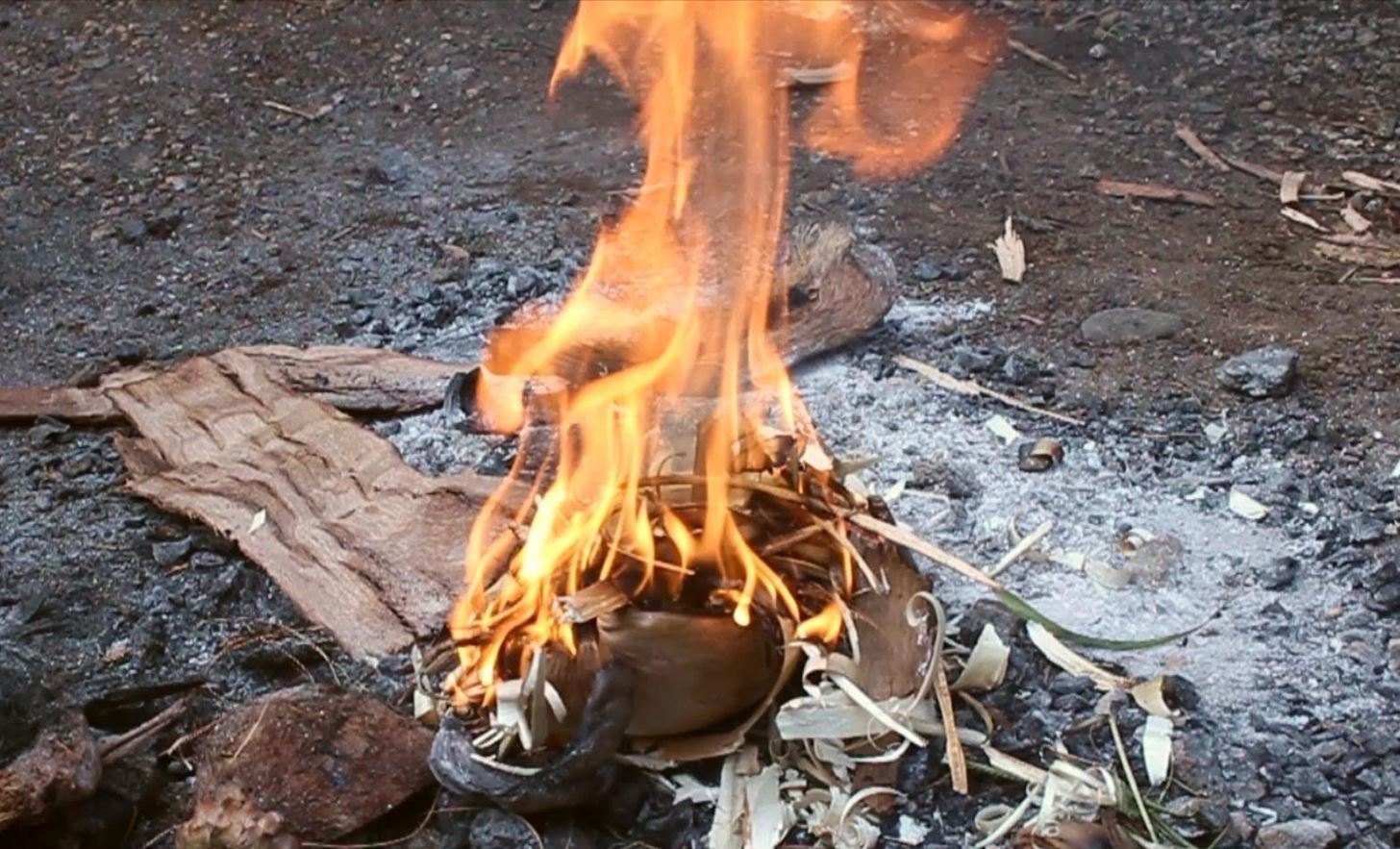
Shelter – Fire Starter/Wet Fire – Sure you can buy waterproof matches, but a fire starter that can never be put out commission in water is supreme and it looks so much cooler when the sparks start to fly. Add to that some wetfire cubes which can even be lit when they are sitting in water and you have the perfect fire making combination. You can also throw all of this in a dry bag for your prepper to add other fire making materials and to keep them organized.
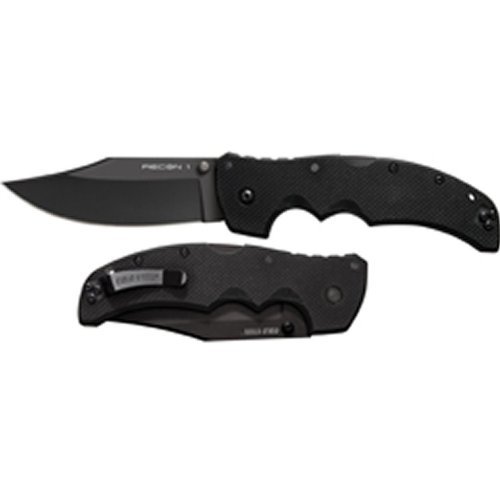
Security – Tactical Folding Knife – I am not sure you can even call yourself a prepper unless you have at least two knives. A good survival knife can help you in so many ways, but you don’t always have to have the most expensive knife in the world. A good quality folding knife can help you cut a lot of things but not break the bank. If they already have a good folding knife, a multi-tool extends their abilities in roughly the same size factor.
X-Factor – Seatbelt cutter – For the Prepper who has almost everything except a seat belt cutter and a glass punch in their favorite bug out vehicle, the resqme (get it?) Keychain car escape tool combines both in a small footprint that is affordable and its compact size makes it easy to add to your preppers EDC kit.
Disaster Scenario #2 – Month Long Viral Outbreak Quarantine
For those preppers on your gift list who are planning for a little longer-term event, they need gear designed to work a little harder or to last a little longer. The following prepper gifts will ensure that your friend will be able to last at least a month before the all clear is given.
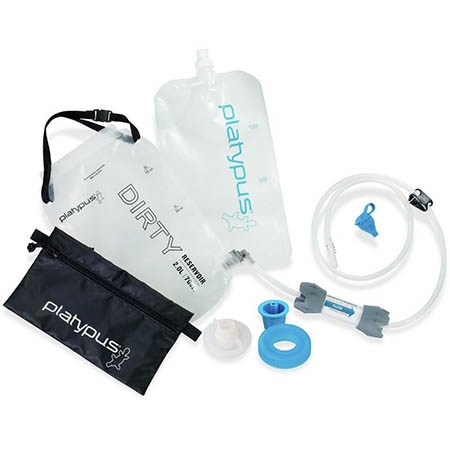
Water– Platypus Gravity Works filter – I fairly recently came across this filter at the suggestion of one of the readers of Final Prepper and I couldn’t be happier. The Gravityworks filters 2 liters of dirty creek water in under 2 minutes. That way I can collect water, stow it my pack, and get back to safety. Unlike chemical treatments like bleach or iodine, there is no bad taste and I don’t have to boil the water and wait for it to cool.
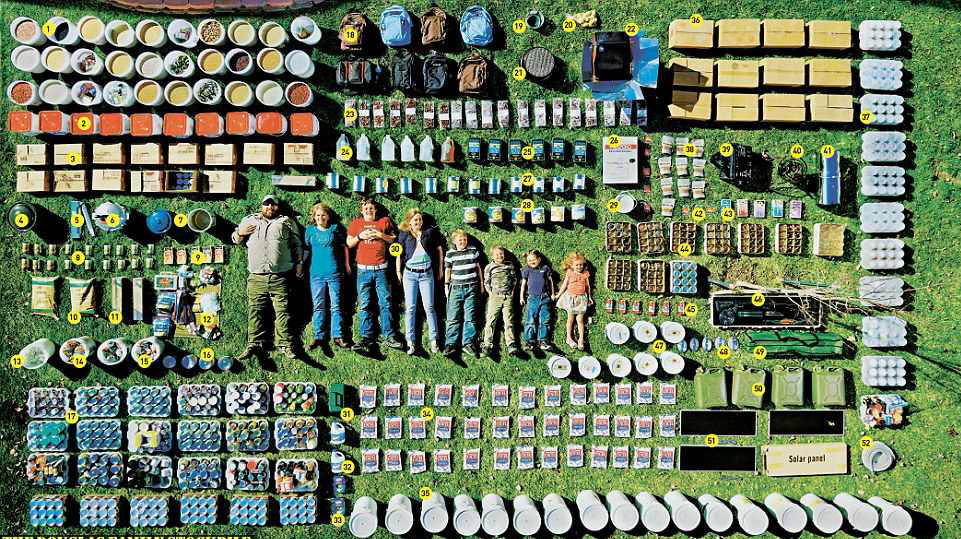
Food – Chef’s Banquet All-purpose Readiness Kit 1 Month Food Storage Supply (330 Servings) – Food storage is on the mind of preppers everywhere, but sometimes you want a simple buy it and forget it option. The benefit of this option is that it comes sealed in its own 5 gallon bucket so all the prepper needs to do is store it in a cool dry place until it is needed. If you purchase more buckets, they will easily stack and reduce your storage footprint.

Month worth of meals in a handy-dandy 5 gallon bucket. When the food is gone, you can use the bucket for a makeshift toilet.
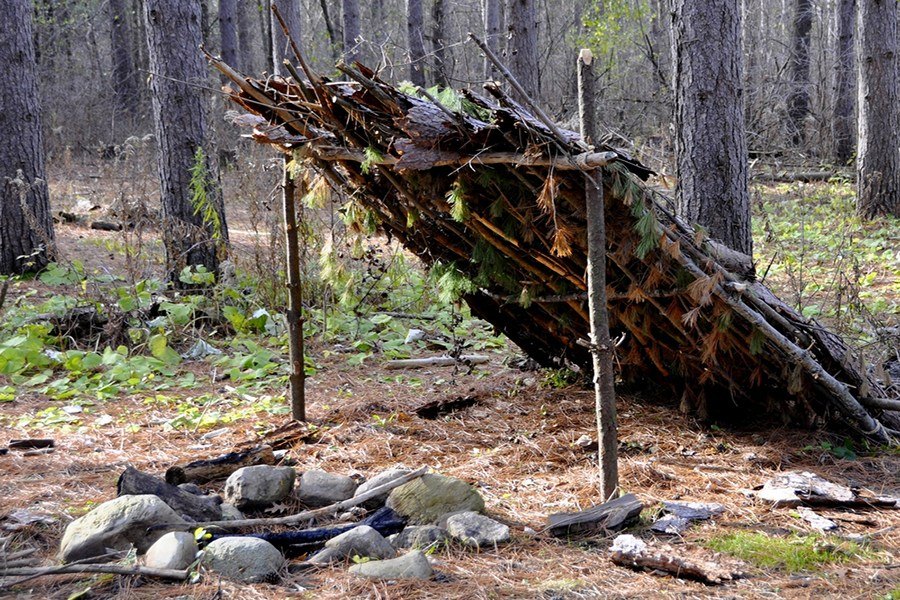
Shelter – 2 Man Tent – It may be that your survival depends on getting out of the city while a virus runs its course. Before you head for the hills, make sure you have a good tent. The Big Agnes Scout UL 2 is a two-man tent that is very lightweight (only 2 pounds!) and compact. Your bug out bag and your back will thank you for switching to this option. Instead of the poles common to most tents, the Big Agnes Scout uses your trekking poles and sheds the weight. You can also just use sticks to prop up the tent or tie one end off to a tree.
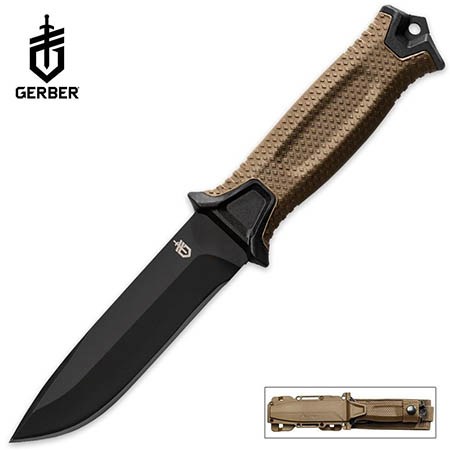
Security – Fixed Blade – Tactical folding knives are great, but if you plan on living in the woods for a month, you will want a bigger, stronger blade. I have the Gerber LMFII but there is a newer Gerber, the Strong Arm 30-001058 that takes some ques from its cousin. This knife will allow you to make firewood by batoning and hold up to a lot of abuse. It even comes with its own sheath that straps to your belt and the Coyote finish should blend in with your surroundings.
X-Factor – Night Vision Monocular – The threats your survivalist is preparing for don’t end when the sun goes down. In order to have an advantage at night, they could use a Night Vision Monocular. This will help them see what is lurking in the dark and give them an upper hand in the fight. This monocular boasts a 1000 ft. viewing distance to help you see what is coming or that big game walking up to your stand from a distance.
Disaster Scenario #3 Total Collapse due to EMP or Zombie Apocalypse
When it has all gone to Sh*t, your prepper gear will be put to the test. Knowledge and training and I would argue, luck are all more important than the price tag of the shiny piece of metal you are carrying in your Get Home Bag. However, longer duration use requires more durable equipment. That tactical folder may be perfect for a weekend, but what would you do if it became damaged? What if your water filter was rendered inoperable due to the high use? Below are some additional prepper gift ideas for the prepper who is planning to ride out the end of the world as we know it.
Water – Big Berkey Water Filter – The water filtration methods I mentioned above are great if you are mobile or only really need to filter water for yourself, maybe another person. If the disaster lasts a long time or you need to filter water for the whole family, day after day, you will need something a little more substantial. The Big Berkey can filter 2.5 gallons at a time and only requires you to pour the unclean water in the top. Gravity does the rest and it even has a handy spout to fill your Nalgene bottles up again with clean filtered water.
Food – Survival Seeds – Yes, the grocery stores are all long plundered of anything you can eat and the burden falls to the prepper to produce food for their family, going forward. A box of Survival Seeds will give them the necessary seeds to start that survival crop; hopefully their garden is already started well before now, but the seeds in this container can be opened in an emergency and provide the ability to grow a big crop of food for the compound. This can also be useful as barter in a pinch.
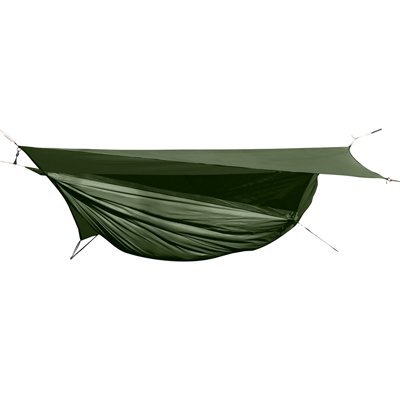
Shelter – Hammock – Tents aren’t meant to last forever but with proper use you can get several seasons out of them. Sleeping on the hard ground is tough though and your prepper might want the comfort of a hammock if they are going to spend the rest of their lives in the woods. A Hennessy Expedition comes with rain fly and a mosquito net to keep the bugs off you and packs down small and light (under 3 pounds) as well making it a great alternative if you are trying to lighten your bug out bag.
Security – Crossbow – Maybe it is the premiere of the new season of the Walking Dead that has me thinking of this item, but a crossbow has a lot of appeal in a grid down/apocalypse scenario. For starters you can hunt very quietly and there is no point in alerting everyone else that you just brought down that big buck. Add to that, when the ammo is all gone, you can still make arrows, if you have the right skill and that could be limitless ammo for your new weapon. Or you could just do what Darryl does and pull each arrow out of the skull of your victim and move on. The Barnett Penetrator Crossbow would do just that with 116 foot pounds of energy, penetrate and could make an excellent weapon in a total collapse. Don’t forget the extra arrows.
Security – Machete/Parang – When all else fails you may need something that can cut a little deeper. From chopping wood to clearing brush or solving problems, permanently, the Parang is a nifty little weapon. Gerber has a nice Parang Machete from Bear Grylls’ line that could help your prepper defend themselves and their family, maybe you from the bad guys. Or zombies.
X-Factor – Gas masks – If the world really has gone to hell, you might need to protect the air you breathe. There could be NBC (nuclear, biological, chemical) agents, viruses, tear gas or who knows what. This Military and Police Tactical mask with the right filters will protect your prepper from inhaling any particles that could bring them down. You can also throw in some Potassium Iodide tablets for a companion gift.
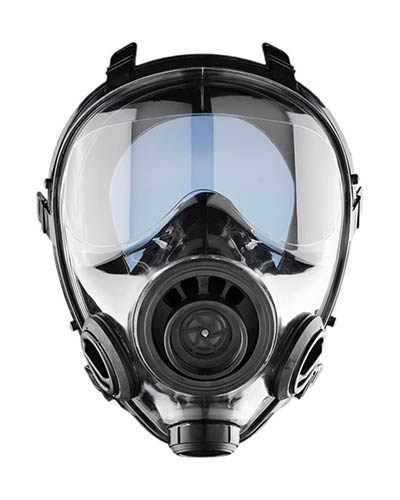

If this comes out, you know it has gotten bad.
So there you have it, my list of over 20 of the best prepper gifts for survival. What’s on your list?
Do you have a prepper on your shopping list? The occasion doesn’t matter really. It could be Mother’s Day, Father’s Day, Christmas or Hanukkah, birthdays or just because. But sometimes